In this article, we’ll define retained earnings, explain how they’re calculated, and examine real-world examples that highlight their significance in financial decision-making. Once you have all of that information, you can prepare the statement of retained earnings by following the example above. When you’re through, the ending retained earnings should equal the retained earnings shown on your balance sheet. Between 1995 and 2012, Apple didn’t pay any dividends to its investors, and its retention ratio was 100%.
Does Capital Stock Affect Retained Earnings? Explained

HAL ERP’s integrated financial management capabilities are ideal for businesses aiming to gain greater control over their finances and boost profitability. With these success stories, discover how organizations across Saudi Arabia are using HAL ERP to strengthen financial operations, enhance retained earnings, and make more confident, data-driven decisions. Understanding the distinction between retained earnings, revenue, and net profit clarifies how profit flows through a business. While revenue reflects top-line income and net profit captures what remains after expenses, retained earnings show how much of that profit is preserved for future use. With this clarity, it’s easier to assess https://kamalsilwal.com.np/manager-of-accounting-services-ecwa-erie-county-2/ the various factors that influence retained earnings over time. It depends on how the ratio compares to other businesses in the same industry.
How retained earnings appear on the balance sheet
Distribution of dividends to shareholders can be in the form of cash or stock. Cash dividends represent a cash outflow and are recorded as reductions in the cash account. These reduce the size of a company’s balance sheet and asset value as the company no longer owns part of its liquid assets. The information about a company’s retained earnings is usually presented in the statement of retained earnings, a part of the company’s financial statements. This statement shows the opening balance, additions to and deductions from the retained earnings, and the closing balance.
Beware of Tax Implications

The entry to correct the error contains a decrease to Retained Earnings on the statement of retained earnings for $1,000. Depreciation expense would have been $1,000 higher if the correct depreciation had been recorded. The entry to Retained Earnings adds an additional debit to the total debits that were previously part of the closing entry for the previous year. The credit is to the balance sheet account in which the $1,000 would have been recorded had the correct depreciation entry occurred, in this case, Accumulated Depreciation. The company will report the appropriate retained earnings in the earned capital section of its balance sheet.
- This flexibility improves operational resilience and positions the business for long-term success.
- The Journal of Accountancy, a periodical published by the AICPA, offers guidance in how to manage this process.
- Retained earnings, on the other hand, represent the total profits reinvested in your company rather than paid out to shareholders as dividends.
- If the result is positive, it means the company has added to its retained earnings balance, while a negative result indicates a reduction in retained earnings.
- Retained Earnings is a permanent equity account aggregating all past income and losses since inception, minus all dividends paid out.
- Retained earnings can also be thought of as the cash reserved for reinvestment in business growth.
- Entity performance affects net income and net losses and the key elements that analysts normally take into accounts, including net income, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and interest expenses.

Below is the balance sheet for Bank of America Corporation (BAC) for the fiscal year ending in 2017, from the bank’s 10K statement. At Profitline, we’re here to help you navigate and optimize retained earnings, ensuring a prosperous future for your business. Such a situation could hinder future investments and expansion plans, impacting long-term sustainability. Maintaining precise financial records is essential for calculating retained earnings accurately. Conversely, a decrease in net income can lead to a decline in retained earnings. Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program.
- Some studies document firms’ choices of accounting method can be related to signaling motives, tax considerations, and market perceptions; this can affect comparability of capital-return metrics.
- If you as a shareholder of the company owned 200 shares, you would then own an 20 additional shares, or a total of 220 (200 + (0.10 x 200)) shares once the company declares the stock dividend.
- For example, management might decide to build up a cash reserve, repay debt, fund strategic investment projects or pay dividends to shareholders.
- The entity may prepare the statement of retained earnings and the balance sheet and the statement of change in equity.
- This is the amount of retained earnings to date, which is accumulated earnings of the company since its inception.
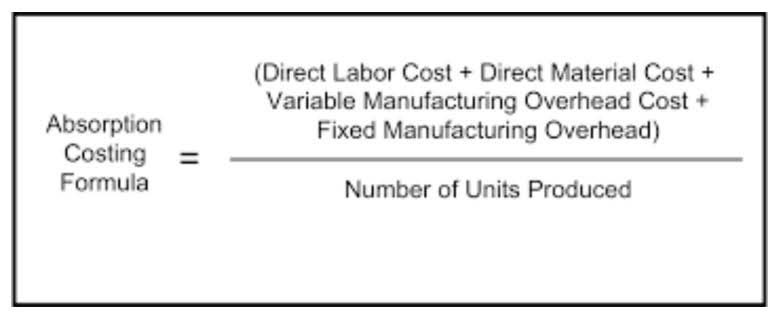
The following is a simple example of calculating retained earnings based on the balance sheet and income statement information. Entity performance affects net income and net losses and the key elements that analysts normally take into accounts, including net income, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and interest expenses. Retained are part of your total assets, though—so you’ll include them alongside your other liabilities if you use the equation above. First, you have to figure out the fair market value (FMV) of the shares you’re distributing. Companies will also usually issue a percentage of all their stock as a dividend (i.e. a 5% stock dividend means you’re giving away 5% of the company’s equity). The difference between what you bring in (revenue) and what you spend (expenses) is your net income.

Revenue and Sales
- Retained earnings are thus a crucial part of financial analysis and provide a key indicator of both historical performance and future potential.
- This can make a business more appealing to investors who are seeking long-term value and a return on their investment.
- This crucial figure is one of the three main components of the equity section on the Balance Sheet.
- This outflow of cash would also lead to a reduction in the retained earnings of the company as dividends are paid out of retained earnings.
- By examining retained earnings over time, investors and management can better understand how effectively a company reinvests profits for growth or rewards shareholders through dividends.
- When you’re able to produce more goods and services, you should be able to expand your company and increase profits.
Bonds, mutual funds, fixed deposits, stocks, real estate, takeovers, petty cash and investing in startups are all ways you can make your money work for you. When this happens, the stock left over — which has suddenly become rarer — often increases in value. With less debt, you should be able to borrow greater loans, pay the money back at a lower interest rate, and grow your business. Below, we discuss what retained earnings are, share an example for how it’s used in context, and explain the formula to calculate your retained earnings.

Below are three concise scenarios showing how treasury transactions flow through equity accounts and when retained earnings can be affected. Retained earnings in the trial balance are the profits that have not been distributed to shareholders but are kept for debt repayment, expansion, and growth. Supplying retained earnings profits is considered the primary objective for most companies and institutions that offer their products and services in the markets. Accurate calculation provides insights into shareholder equity and overall business performance. Negative retained earnings serve as a red flag, indicating potential issues that need prompt attention for long-term sustainability.